2026-02-02
When Postdoctoral Research Fellow Hannah Youngblood’s work on exfoliation glaucoma (XFG) was featured by the BrightFocus Foundation, it caught the attention of Jennifer Rucker, an Alabama resident who was diagnosed with XFG several years ago.
2026-02-26
The professors have been recognized for patenting and commercializing technologies with real-world impact.
2026-02-18
It is the highest degree of membership awarded by the society.
2026-02-17
The fellowship is one of the most competitive and prestigious awards available to early-career scholars.
2026-01-28
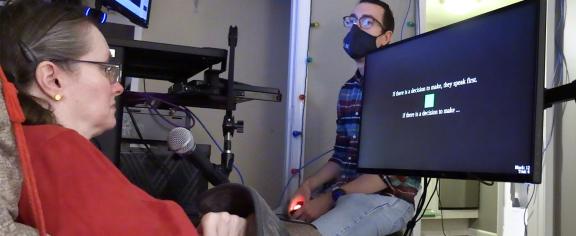
Biomedical engineer Chethan Pandarinath collaborates with neurosurgeons and scientists across the country in a massive project to help patients with ALS or stroke damage reconnect with the world.
2026-01-08
By studying the way social forces shape health inequalities, medical sociology helps address how health and illness extend beyond the body and into every aspect of people’s lives.
2025-12-16
Studying how mice see has helped researchers discover unprecedented details about how individual brain cells communicate and work together to create a mental picture of the visual world.
2025-11-24
By uniting expertise and resources, Georgia’s leading institutions are creating practical solutions to improve health outcomes across the state.
2025-10-27
AI-powered artificial muscles made from pliable materials are reshaping recovery, from stroke rehabilitation to prosthetic design. These machines help people regain motion, strength, and confidence.
2025-10-23
Researchers analyzed data from 10, yurt-like test chambers in a natural boreal spruce bog in northern Minnesota.